import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sb
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltOntario Research Fund - Research Excellence Program - Open Ontario
Data Provider
The provincial government of Ontaio provides open access to thousands of data sets via their Open Data Ontario portal. The purpose of sharing all data documents with the public is to remain transparent and accessible. More details about the data license, training materials, and other information can be found here.
Ontario Research Fund - Research Excellence Program
This Ontario Research Fund dataset includes research projects funded through the Research Excellence Program from 2003 to 2018. The first row of the dataset provides the column names. The variables include research program titles and descriptions, approval date, lead research institution and city where the institution located, total project costs, and Ontario funding commitment.
The dataset and its supporting document can be found here and you can quickly preview the CSV dataset file here. Moreover, The legend description can be viewed here
Libraries
library(tidyverse)
library(lubridate)
library(viridis)
library(hrbrthemes)
library(ggridges) Organizing Dataset
The following code is used to download the dataset, pick important variables to form a new dataset and convert some variables from character format into their specific one.
The head of the well-organized dataset is shown at the end of the code and from that, we can easily found those most important variables. After forming the new dataset, the rest of the paper is going to use this dataset to create some graphs.
# Download the CSV file and organize the dataset
data = pd.read_csv("https://files.ontario.ca/opendata/orfre_apr_20_18_0.csv",
skiprows=1,
encoding='unicode_escape')
# Get rid of empty rows and change the formats of date and currency variables
data = data.dropna(subset = ["Program"])
data["Ontario Commitment"] = data["Ontario Commitment"].replace({'\$': '',
',': ''},
regex=True)
data["Total Project Costs"] = data["Total Project Costs"].replace({'\$': '',
',': ''},
regex=True)
data["Ontario Commitment"] = data["Ontario Commitment"].astype(int)
data["Total Project Costs"] = data["Total Project Costs"].astype(int)
data["Approval Date"] = pd.to_datetime(data["Approval Date"])<string>:3: UserWarning: Could not infer format, so each element will be parsed individually, falling back to `dateutil`. To ensure parsing is consistent and as-expected, please specify a format.data.head() Program ... OIA_AREA
0 ORF RE ... Advanced health technologies
1 ORF RE ... Digital media and information and communicatio...
2 ORF RE ... Bio-economy and clean technologies
3 ORF RE ... Digital media and information and communicatio...
4 ORF RE ... Advanced health technologies
[5 rows x 21 columns]# Plot the Paired graph
# Extract the year from the approval date
data["year"] = data["Approval Date"].dt.year
sb.set_style("darkgrid")
sb.boxplot(data=data,
x="year",
y="Ontario Commitment",
orient="v")
plt.title("Funding per Year (From Ontario)")
plt.xlabel("Year of Approval")
plt.ylabel("Dollars of Funding")
plt.show;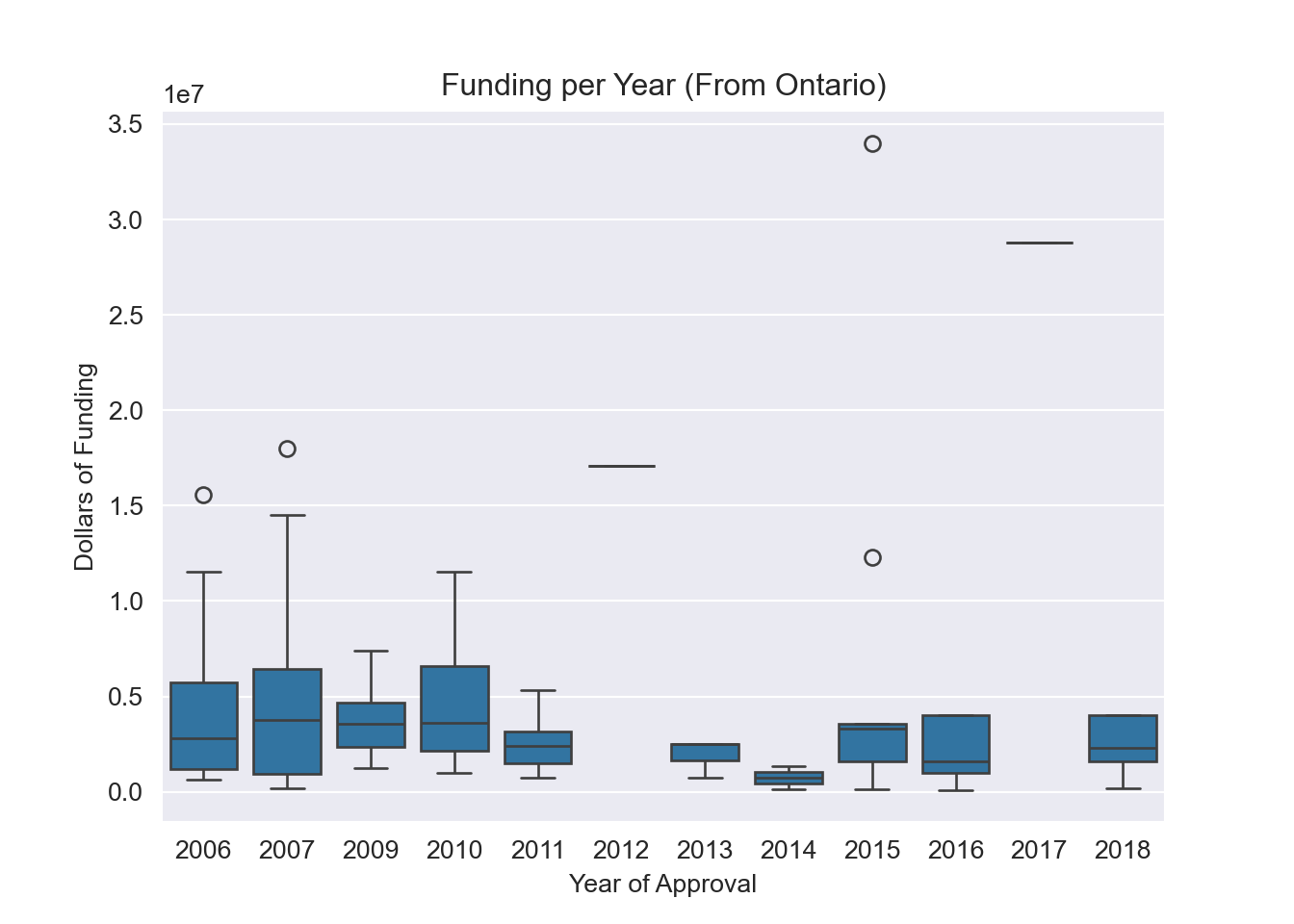
# Download the CSV file and organize the dataset
data <- read_csv("https://files.ontario.ca/opendata/orfre_apr_20_18_0.csv", skip=1)
# Get rid of empty rows and change the formats of date and currency variables
data <- data |> rename_all(make.names)|>
subset(Program!="") |>
mutate(Ontario.Commitment = as.numeric(gsub("[$,]", "", Ontario.Commitment))) |>
mutate(Total.Project.Costs = as.numeric(gsub("[$,]", "", Total.Project.Costs))) |>
mutate(Approval.Date = as.Date(Approval.Date, "%d-%b-%y"))
head(data)# A tibble: 6 × 21
Program Project.Number Project.Title Project.Description Area.Primary
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
1 ORF RE RE01-076 Structural and Functi… "Dr. Robert Hegele… 4.1
2 ORF RE RE01-025 Intelligent Multiple … "Global wireless t… 7.6.2
3 ORF RE RE01-063 The Ontario BioCar In… "Manufacturing and… 7.5.2
4 ORF RE RE01-065 SHARCNET: New Opportu… "The Shared Hierar… 7.6.3
5 ORF RE RE01-067 Centre for Brain and … "Dr. Melvyn A. Goo… 4.1
6 ORF RE RE01-027 Thermo-mechanical Des… "Hydrogen has pote… 5.7
# ℹ 16 more variables: Area.Secondary <chr>, Discipline.Primary <dbl>,
# Discipline.Secondary <dbl>, Round <chr>, Approval.Date <date>,
# Lead.Research.Institution <chr>, City <chr>, Ontario.Commitment <dbl>,
# Total.Project.Costs <dbl>, Keyword <chr>, EXPENDITURE_TYPE <chr>,
# Salutation <chr>, First_Name <chr>, Middle_Name <chr>, Last_Name <chr>,
# OIA_AREA <chr># Plot the Paired graph
#extract the year from the approval date
data |>
separate(Approval.Date, into = c("year","month", "date"), sep = "-")|>
ggplot( )+
#geom_point(aes(x=year, y=Ontario.Commitment))+
geom_boxplot(aes(y=Ontario.Commitment, x=factor(year)))+
ggtitle("Funding per Year (From Ontario)")+
labs(y="Dollars of funding", x = "Year of approval")+
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, vjust = 0.5, hjust=1))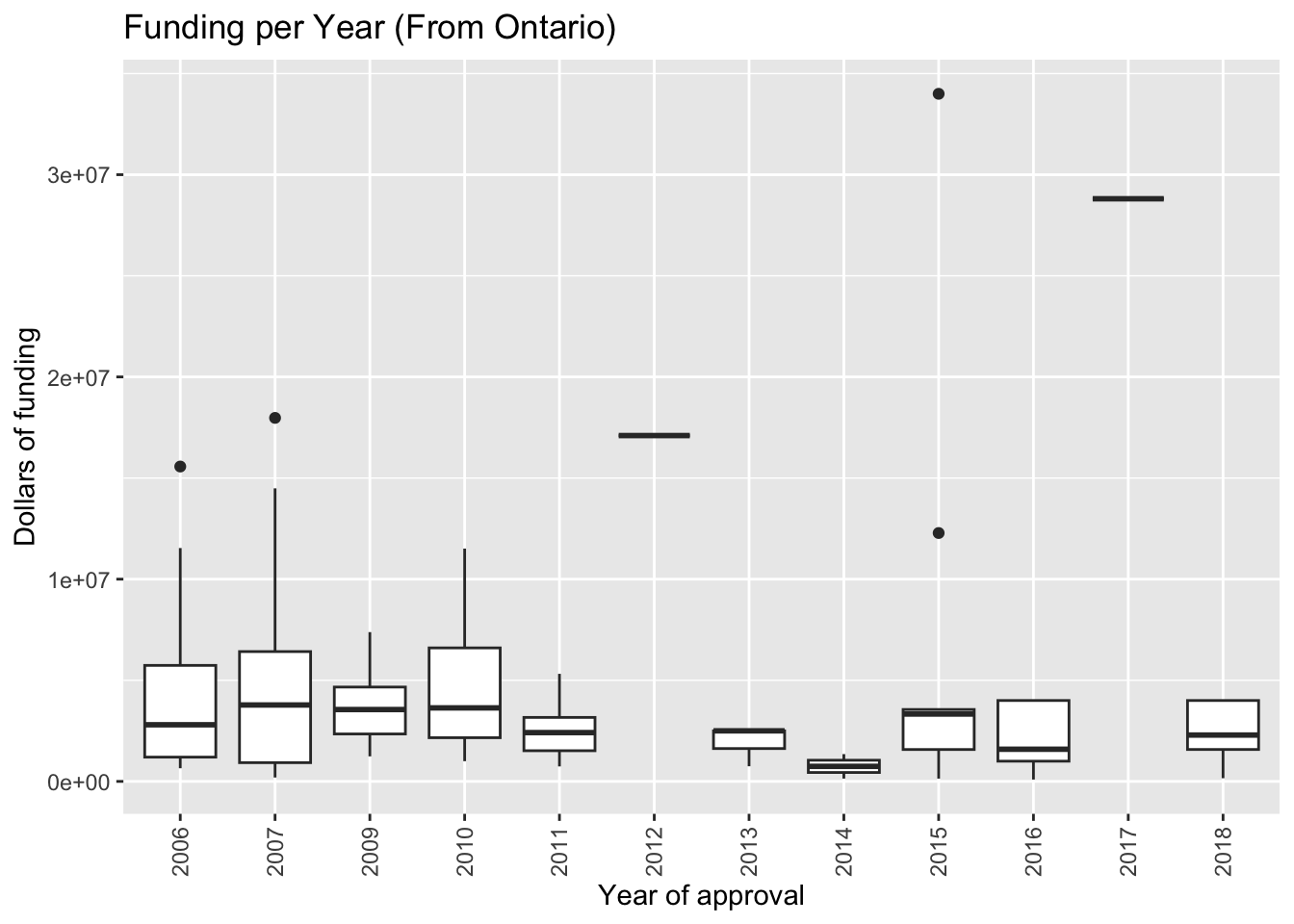
- The graph shows that most of the projects were for $1,000,000 - $4,000,000 Canadian dollars.
Frequency of Study Area
The following code is used to draw the different research areas funding. Note that first we need to sum within each category (OIA_AREA) and then fill in the table so that we have zeros in all the missing years.
total_funding = data.groupby(["year", "OIA_AREA"],
as_index=False)['Ontario Commitment'].sum()
plt.clf()
sb.lineplot(data = total_funding,
x = "year",
y = "Ontario Commitment",
hue = "OIA_AREA")
plt.title("Total Funding Per Year Within Each Category")
plt.ylabel("Total Funding")
plt.legend(title = "OIA Area",
bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1),
loc='upper left',
borderaxespad=0);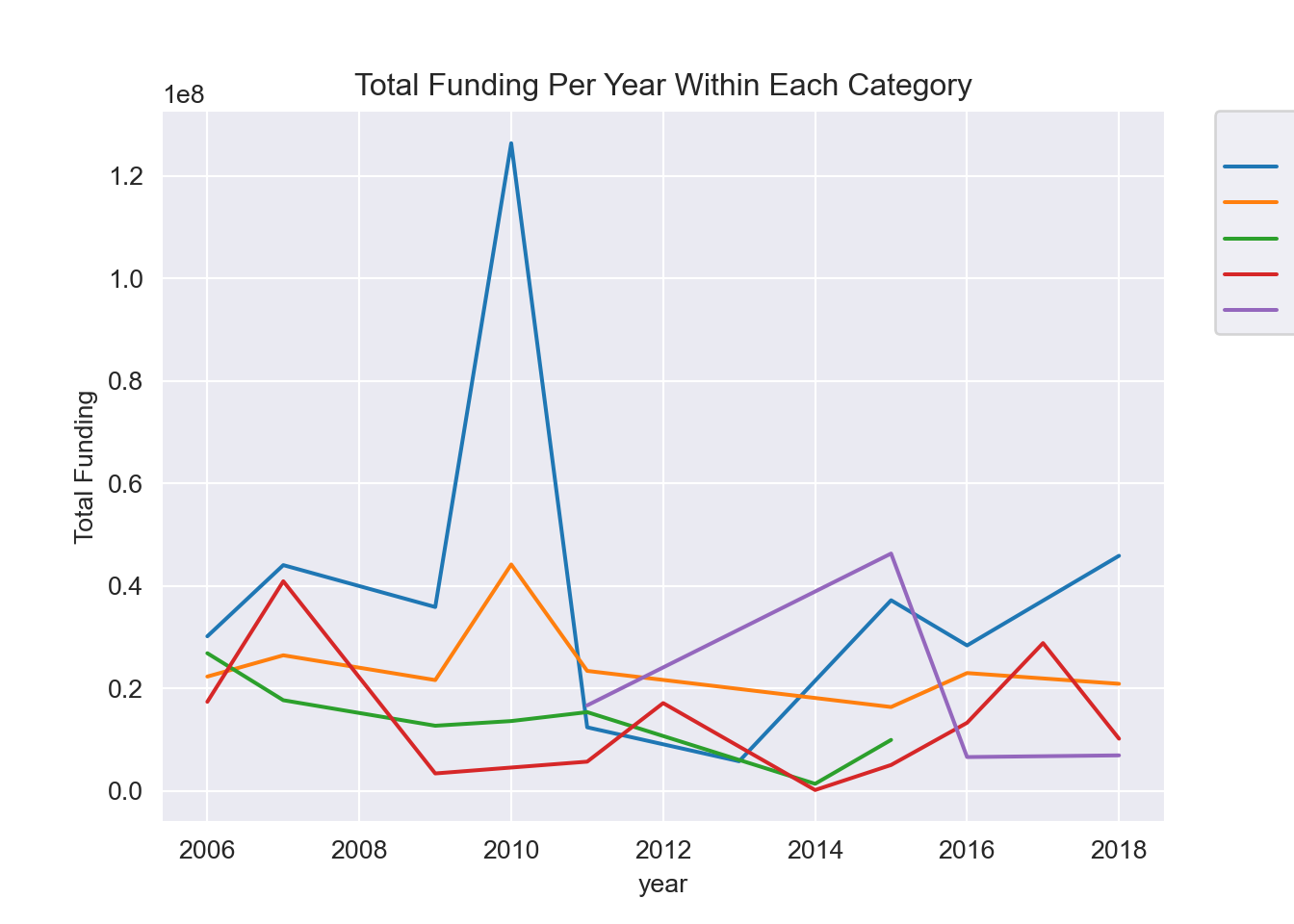
data |>
separate(Approval.Date, into = c("year","month", "date"), sep = "-")|>
group_by(year,OIA_AREA) |>
summarize(TotalFunding = sum(Ontario.Commitment))|>
ungroup()|>
complete(OIA_AREA,year,fill = list(TotalFunding = 0))|>
ggplot( aes(x=year, y=TotalFunding, group=OIA_AREA )) +
geom_line(aes(color = OIA_AREA)) +
ggtitle("Total Funding Per Year Within Each Category")+
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, vjust = 0.5, hjust=1))`summarise()` has grouped output by 'year'. You can override using the
`.groups` argument.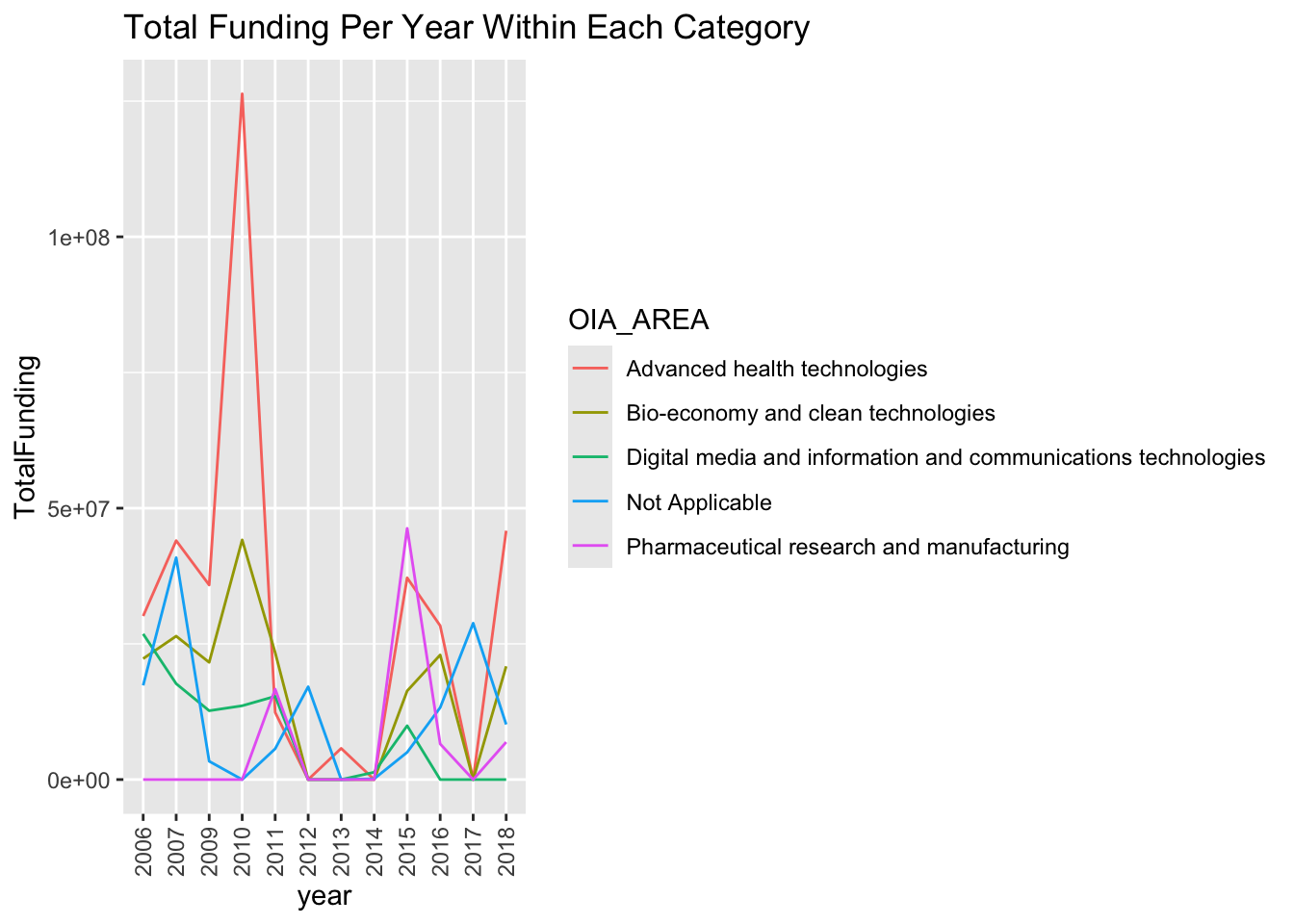
Summary
- Research programs are separated into 5 areas: Advanced health technologies, Bio-economy and clean technologies, Digital media information and communications technologies, Pharmaceutical research and manufacturing, and other unspecified groups. Not all programs were active every year.
proportions = total_funding.pivot_table(index=['year'],
columns = 'OIA_AREA',
values ='Ontario Commitment').reset_index().set_index('year').fillna(0)
proportions = proportions.div(proportions.sum(axis=1), axis=0)
plt.clf()
proportions.plot(kind='bar', stacked = True)
plt.title("Funding proportion in each research area")
plt.xlabel("Year")
plt.ylabel("Proportion of Funding")
plt.legend(title="OIA Area",
bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1),
loc='upper left',
borderaxespad=0)
plt.show();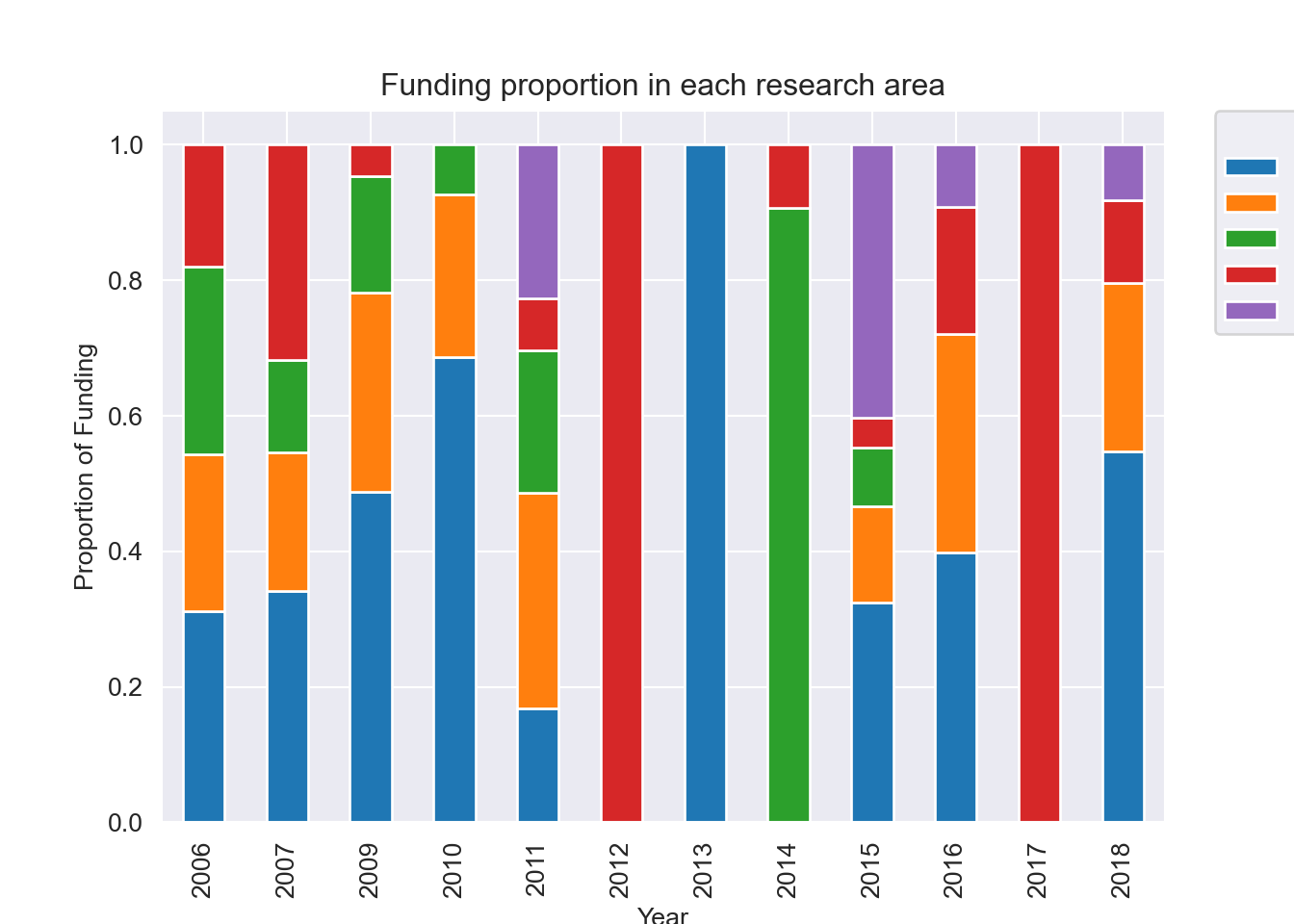

# percentage of study are in research fund
data |>
separate(Approval.Date, into = c("year","month", "date"), sep = "-")|>
group_by(year,OIA_AREA) |>
summarize(TotalFunding = sum(Ontario.Commitment))|>
ungroup()|>
complete(OIA_AREA,year,fill = list(TotalFunding = 0))|>
ggplot( aes(x = year,fill=OIA_AREA, y=TotalFunding)) +
geom_bar(position="fill", stat="identity") +
scale_fill_viridis(discrete = T) +
ggtitle("Funding proportion in each research area ") +
theme_ipsum() +
xlab("year")+
ylab("proportion of funding")+
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 90, vjust = 0.5, hjust=1))`summarise()` has grouped output by 'year'. You can override using the
`.groups` argument.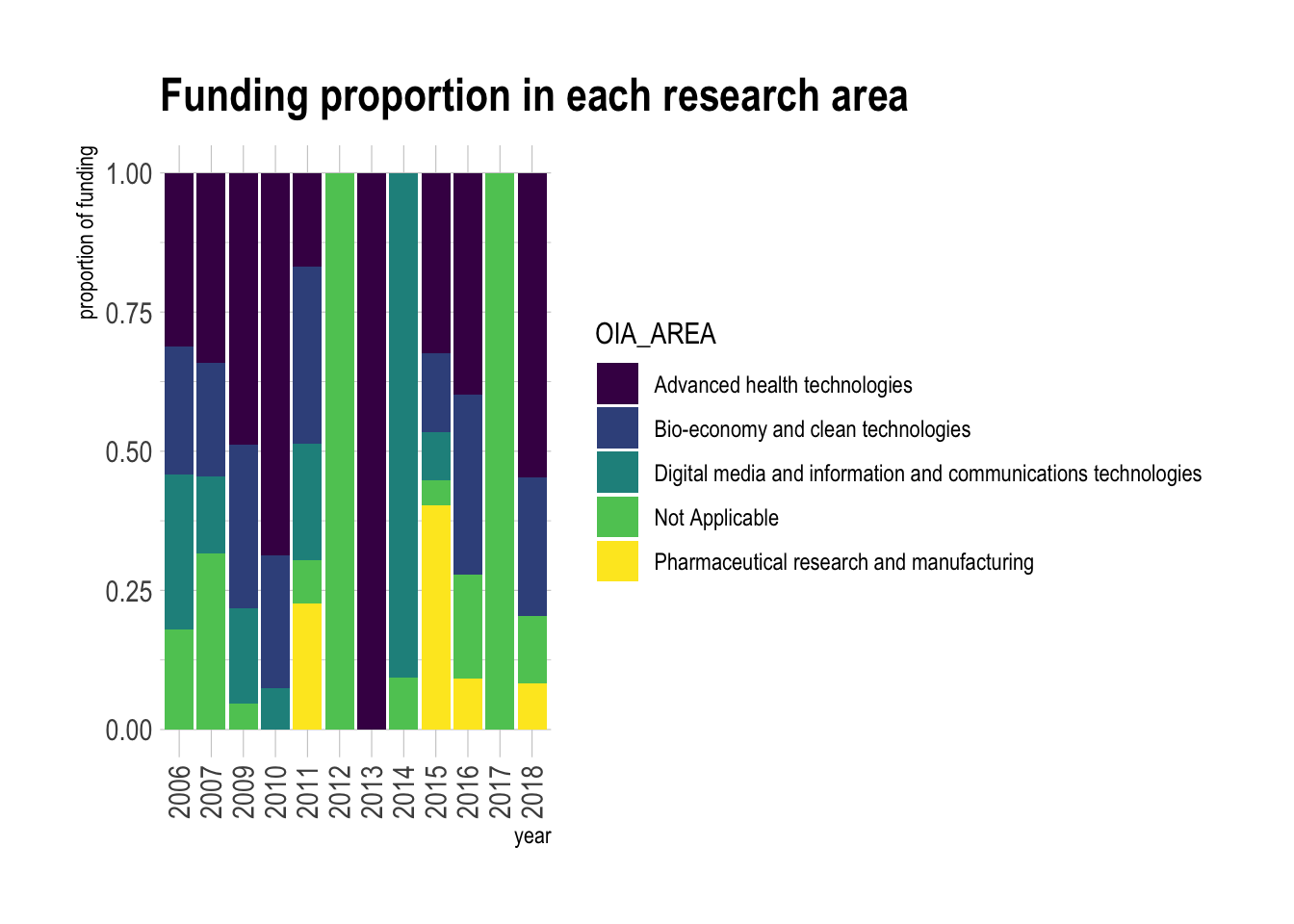
Frequency distribution of research projects grouped by cities and Lead Research Institutions
The following codes are used to plot the ridgeline graphs about the frequency of research projects by cities and Lead Research Institutions.
# Create their own summarized table
# Count projects per year for each institution
ins = data[['year', 'Lead Research Institution']].value_counts().reset_index(name = 'count')
# Get frequency of counts
ins2 = ins[['count', 'Lead Research Institution']].value_counts().reset_index(name = 'freq')
ins3 = ins2.pivot_table(values = 'freq', index = "Lead Research Institution", columns = 'count').fillna(0)
# Add in frequency of 0 project years for each institute
ins3[0] = 13 - sum(ins3[i] for i in range(1,9))plt.clf()
sb.set_style('white')
for i in range(30):
plt.subplot(30,1,i+1)
sb.barplot(data = ins3.iloc[i],
width = 0.2)
plt.legend('', frameon = False)
plt.xlabel('')
plt.ylabel(ins3.index[i], rotation = 0, ha = 'right', va = 'center')
plt.yticks([])
sb.despine(left = True)
if i != 29:
plt.xticks([])
if i == 29:
plt.xlabel("Number of approved research projects in a year")
plt.show();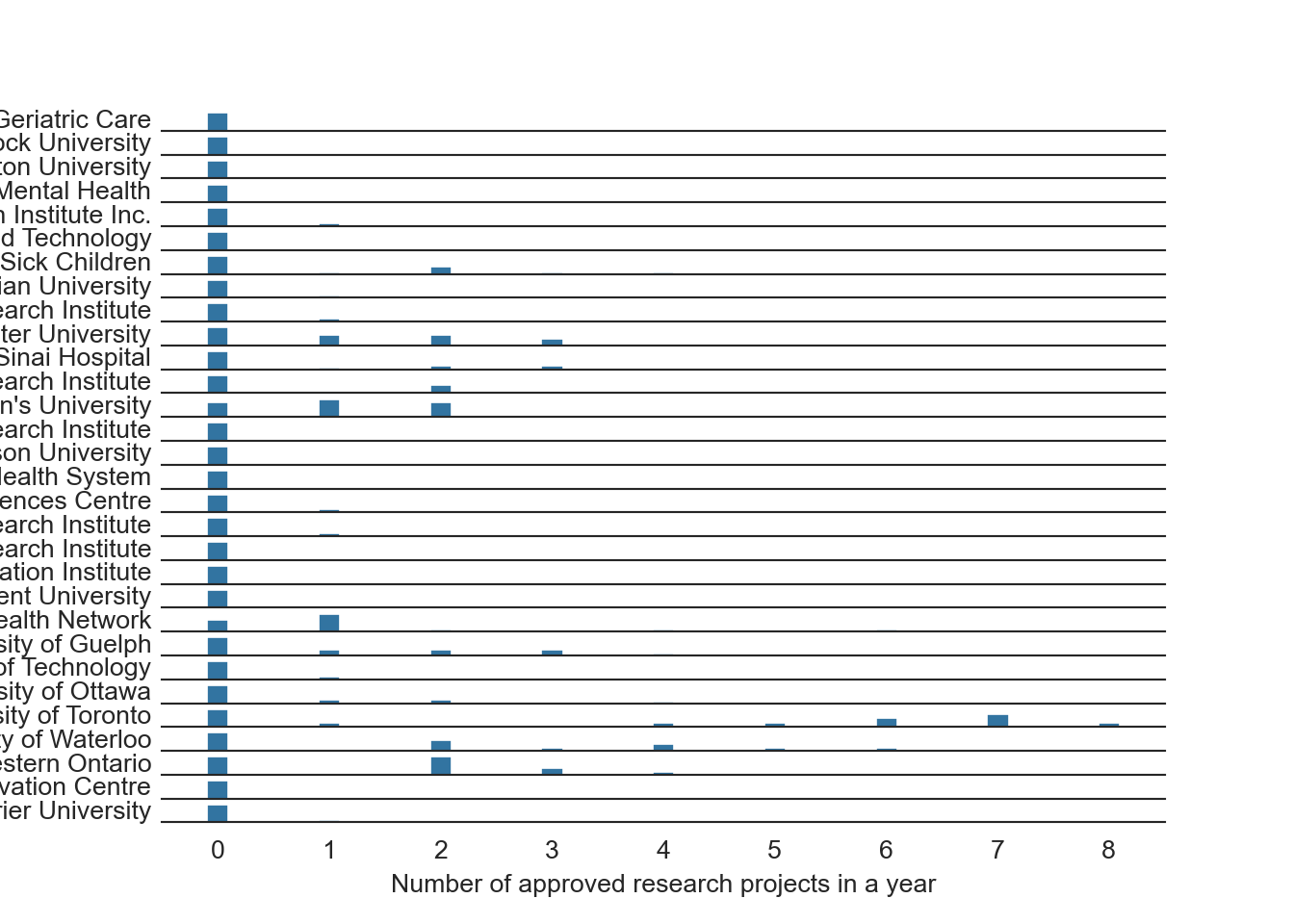
# Count projects per year for each institution
city = data[['year', 'City']].value_counts().reset_index(name = 'count')
# Get frequency of counts
city2 = city[['count', 'City']].value_counts().reset_index(name = 'freq')
city3 = city2.pivot_table(values = 'freq', index = "City", columns = 'count').fillna(0)
# Fill in years where num projects was 0
for i in [7,8,9,10,14,15,16,19,20,21]:
city3[i] = 0
# Add in frequency of 0 project years for each institute
city3[0] = 13 - sum(city3[i] for i in range(1,23))plt.clf()
sb.set_style('white')
for i in range(13):
plt.subplot(13,1,i+1)
sb.barplot(data = city3.iloc[i],
width = 0.2)
plt.legend('', frameon = False)
plt.xlabel('')
plt.ylabel(city3.index[i], rotation = 0, ha = 'right', va = 'center')
plt.yticks([])
sb.despine(left = True)
if i != 12:
plt.xticks([])
if i == 12:
plt.xlabel("Number of approved research projects in a year")
plt.show();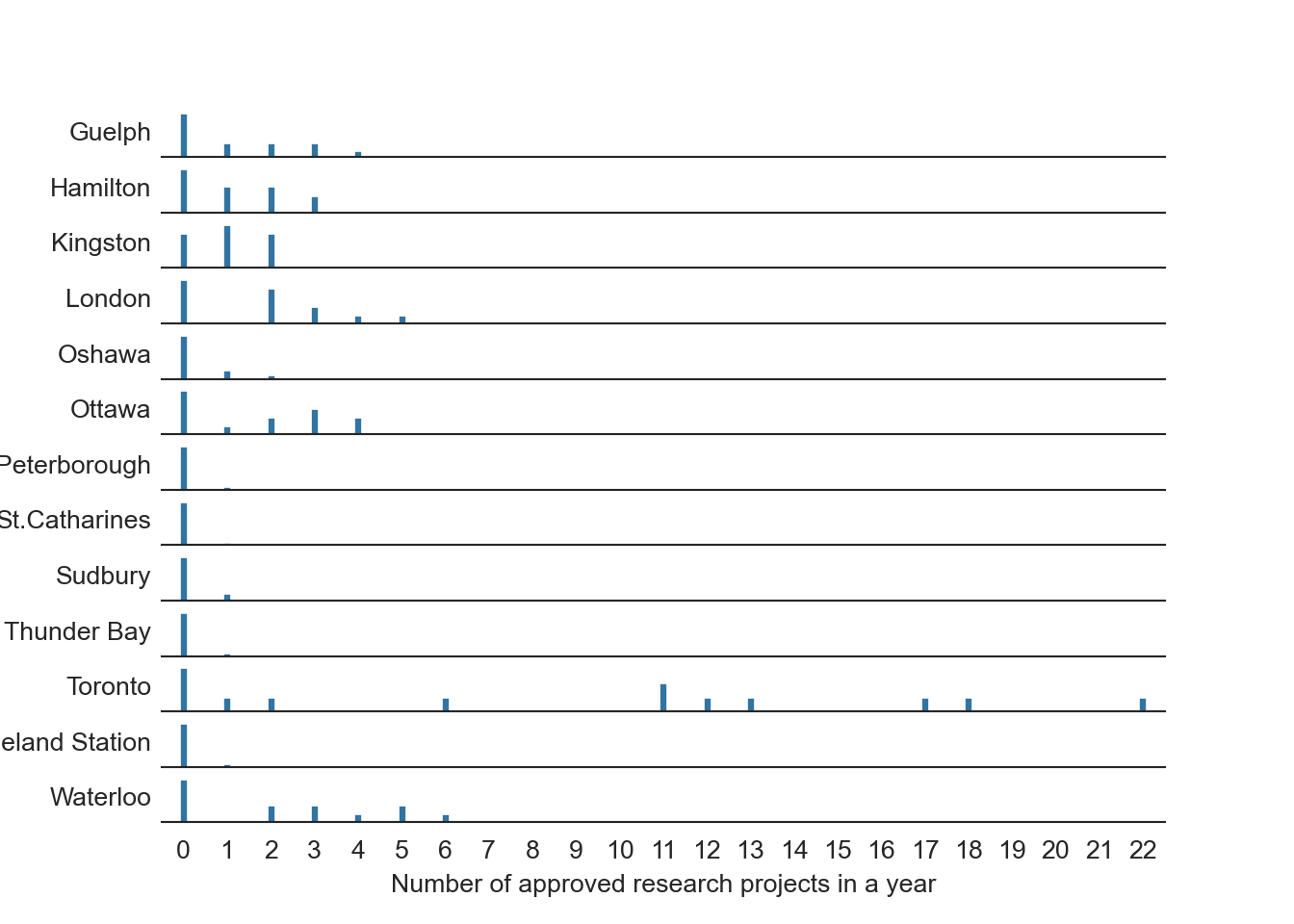
# Create thier own summarized table
ins = data |>
separate(Approval.Date, into = c("year","month", "date"), sep = "-")|>
group_by(year,Lead.Research.Institution) |>
tally() |>
ungroup()|>
complete(Lead.Research.Institution,year, fill = list(n = 0))
city = data |>
separate(Approval.Date, into = c("year","month", "date"), sep = "-")|>
group_by(year,City) |>
tally()|>
ungroup()|>
complete(City,year, fill = list(n = 0))
# Plot their ridgeline graphs
ins |>
ggplot(aes(y=Lead.Research.Institution, x=n, fill=Lead.Research.Institution)) +
geom_density_ridges(alpha=0.6, stat="binline", bins=20) +
theme_ridges() +
theme(legend.position="none",
panel.spacing = unit(0.1, "lines"),
strip.text.x = element_text(size = 3)) +
xlab("Number of approved research projects in a year") +
ylab("Lead Research Institution")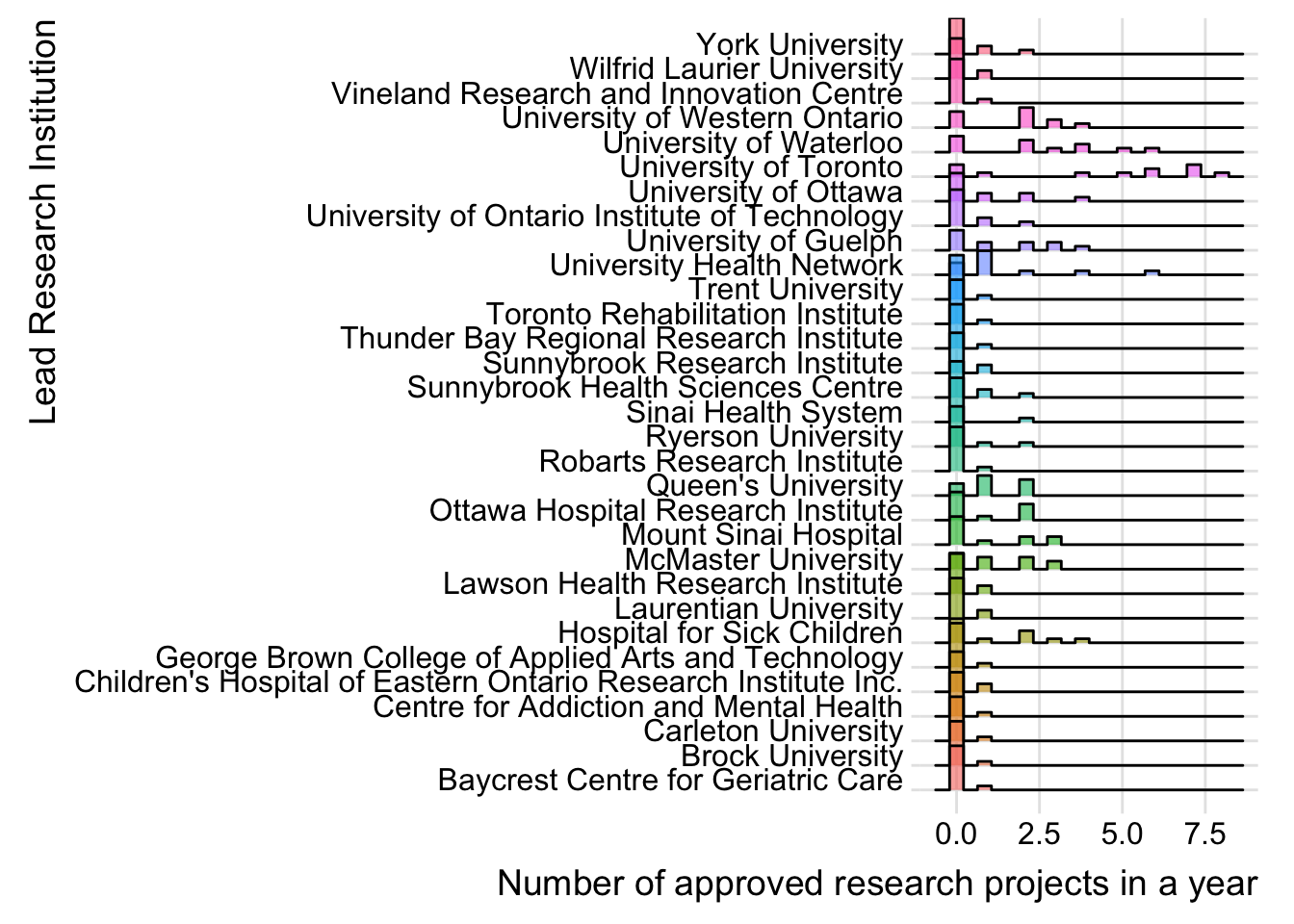
city |>
ggplot(aes(y=City, x=n, fill=City)) +
geom_density_ridges(alpha=0.6, stat="binline", bins=20) +
theme_ridges() +
theme(legend.position="none",
panel.spacing = unit(0.1, "lines"),
strip.text.x = element_text(size = 3)) +
xlab("Number of approved research projects in a year") +
ylab("City")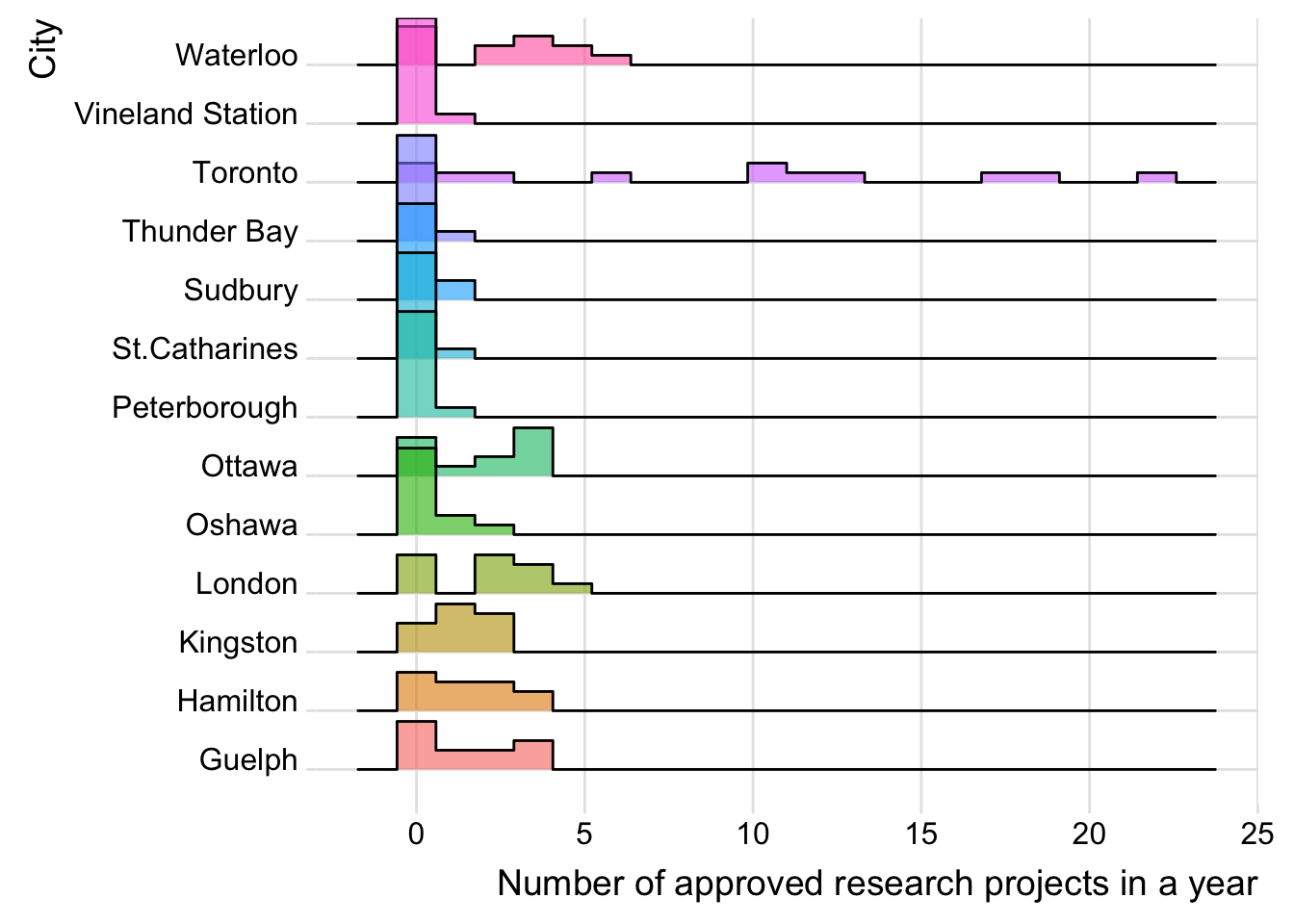
Summary
- The graph counts the number of approved projects by cities and Lead Research Institutions, essentially a histogram of approvals within each year. There are many years in which the values are zero for a city or institution so these must be re-included, otherwise the data will be misleading.