#libraries
import os
import requests
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sb
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltEnvironment Canada Weather Station Data
Data Provider
Environment Canada records maintains records of historical weather variables. The available data sets include as monthly summaries, averages, extremes values of temperature, precipitation, degree days, relative humidity, wind speed, and direction among 370 city stations in Canada. The dataset and its description file can be found here.
You also can search for historical climate data by station name and date, province/territory, or do a proximity search.
Climate Data: Daily Weather Report
This dataset shows the basic historical weather data in a specific climate station. Both climate ID and TC ID are used to identify meteorological reports, one is assigned by Meteorological Service of Canada, another is assigned by Transport Canada. More glossary can be found here.
The daily climate data in Ottawa is summarized via the Max, Min, and Mean Temperatures, as well as Heat and Cool Degree Days. Data is also collected for the speed and direction of maximum gust when the maximum gust speed exceeds 29 km/h. The data source can be downloaded in CSV form, you can modify the code to download monthly data files, with additional instructions in the “readme.pdf” file here.
Libraries
#libraries
library(tidyverse)
library(lubridate)
library(RColorBrewer)RestAPI
The weather station, year, and time resolution are all defined by the url as a RestAPI. We need to loop over a list of urls for different years and download the linked files into the “Data” directory. The urls change with parameters:
- timeframe=2 returns 1 year of daily data.
- timeframe=3 returns monthly for as many years as is available.
- Year defines a single year of data to return. Omitting this argument and requesting monthly data returns all available years.
- Month and Day are the numeric date values of the start of the data.
- stationID can be found in the Station Inventory EN.csv file alongside the RestAPI instructions here. This file also provides the associated start and end years for historic data, Latitude, Longitude, and elevation for each station.
base_url = ["https://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_data/bulk_data_e.html?format=csv&stationID=4333&Year=", "&Month=1&Day=1&timeframe=2&submit=Download+Data"]
for year in range(1970, 2023):
r = requests.get(base_url[0] + str(year) + base_url[1])
with open("Data/Ottawa" + str(year) + "-daily.csv", "wb") as file:
file.write(r.content)Or download a single year of daily data
base_url2 = "https://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_data/bulk_data_e.html?format=csv&stationID=4333&timeframe=3&submit=Download+Data"
r = requests.get(base_url2)
with open("Data/Ottawa-monthly.csv", "wb") as file:
file.write(r.content)#Obtain daily data:
base_url = c("https://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_data/bulk_data_e.html?format=csv&stationID=4333&Year=", "&Month=1&Day=1&timeframe=2&submit=Download+Data")
# Note:
#timeframe=2 = daily
#timeframe=3 = monthly
destfile = list()
for(year in 1970:2023){
download.file(paste0(
base_url[1],year,
base_url[2]),
destfile = paste0("Data/Ottawa",year,"-daily.csv"))
}
#Obtain monthly data from 1883 - 2006
base_url2 = c("https://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_data/bulk_data_e.html?format=csv&stationID=4333&timeframe=3&submit=Download+Data")
download.file(base_url2,
destfile = paste0("Data/Ottawa-monthly.csv"))Exploratory Analysis
Loading and compiling the daily data
To load the daily data into a dataframe, we loop over all the files in the current working directory and add all files ending in daily.csv to a list. We then pass this list to the pandas concatenate function which will combine all the given files into a dataframe.
# Find all csv files in the "Data" folder.
filepaths = ["Data/"+f for f in os.listdir("Data") if f.endswith('-daily.csv')]
df = pd.concat(map(pd.read_csv, filepaths), ignore_index = True)
df["Date/Time"] = pd.to_datetime(df["Date/Time"])files2load = list.files(path="Data",pattern="daily")
# Big loop to load and append all files,
# but first extract the data types from the most year:
data_daily = read_csv(paste0("Data/",tail(files2load,1)))
columntypes = data_daily %>% summarise_all(class) |> as.list()
# then use bind_rows to ensure all columns are properly aligned:
for(year in 1:(length(files2load)-1)){
data_daily = bind_rows(data_daily,
read_csv(paste0("Data/",files2load[year]),
col_types = columntypes))
}Plots
sb.set_style("darkgrid")
sb.lineplot(data = df,
x = "Date/Time",
y = "Mean Temp (°C)",
hue = "Year")
plt.legend('', frameon = False)
plt.title("Daily Mean Temperatures")
plt.show();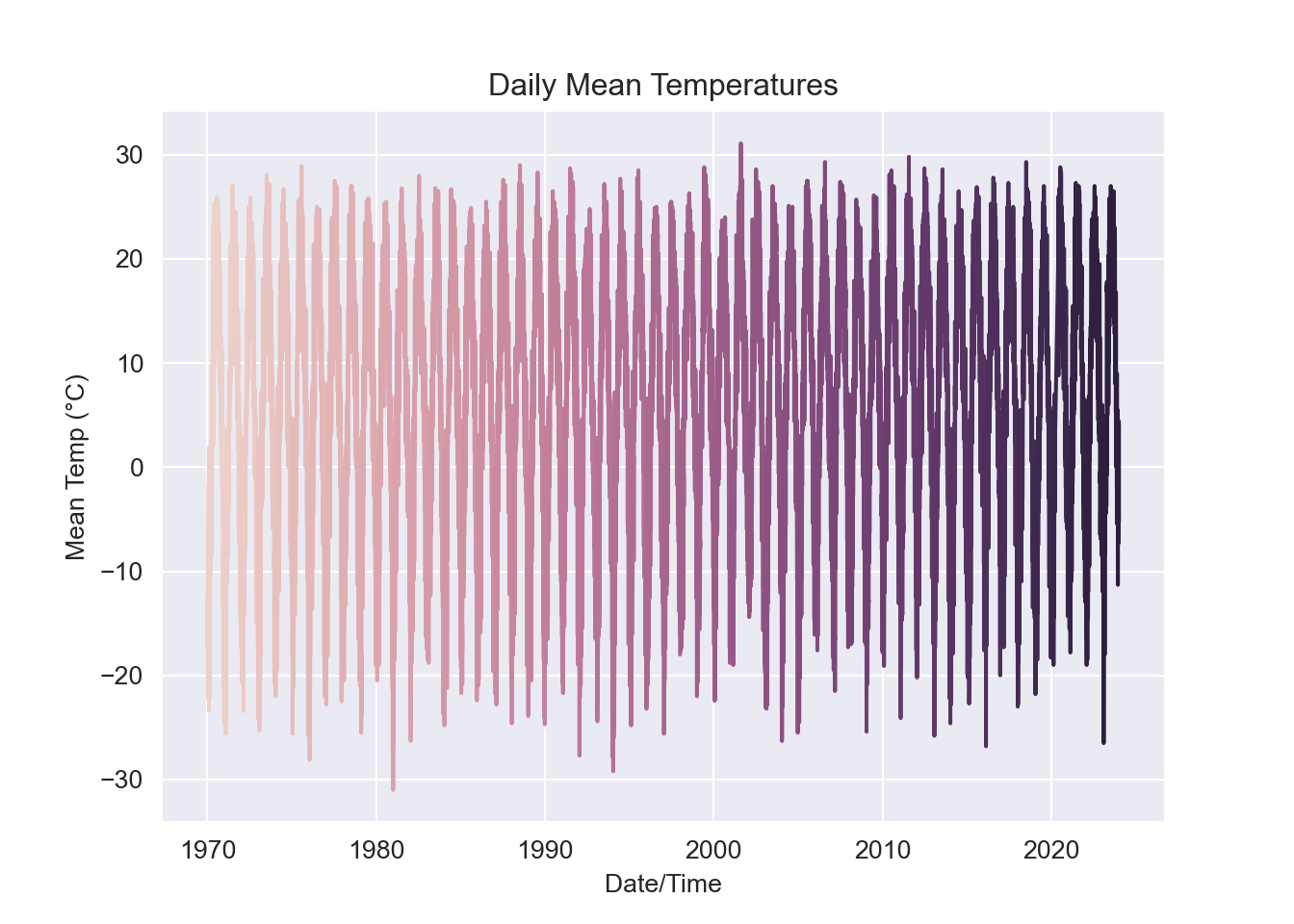
# convert all column names to valid R syntax:
data_daily = data_daily |> rename_all(make.names)
ggplot(data_daily,aes(x=Date.Time,y=Mean.Temp...C.,colour=factor(Year)))+
geom_line()+
ggtitle("Daily Mean Temperatures")+
theme(legend.position = "none") 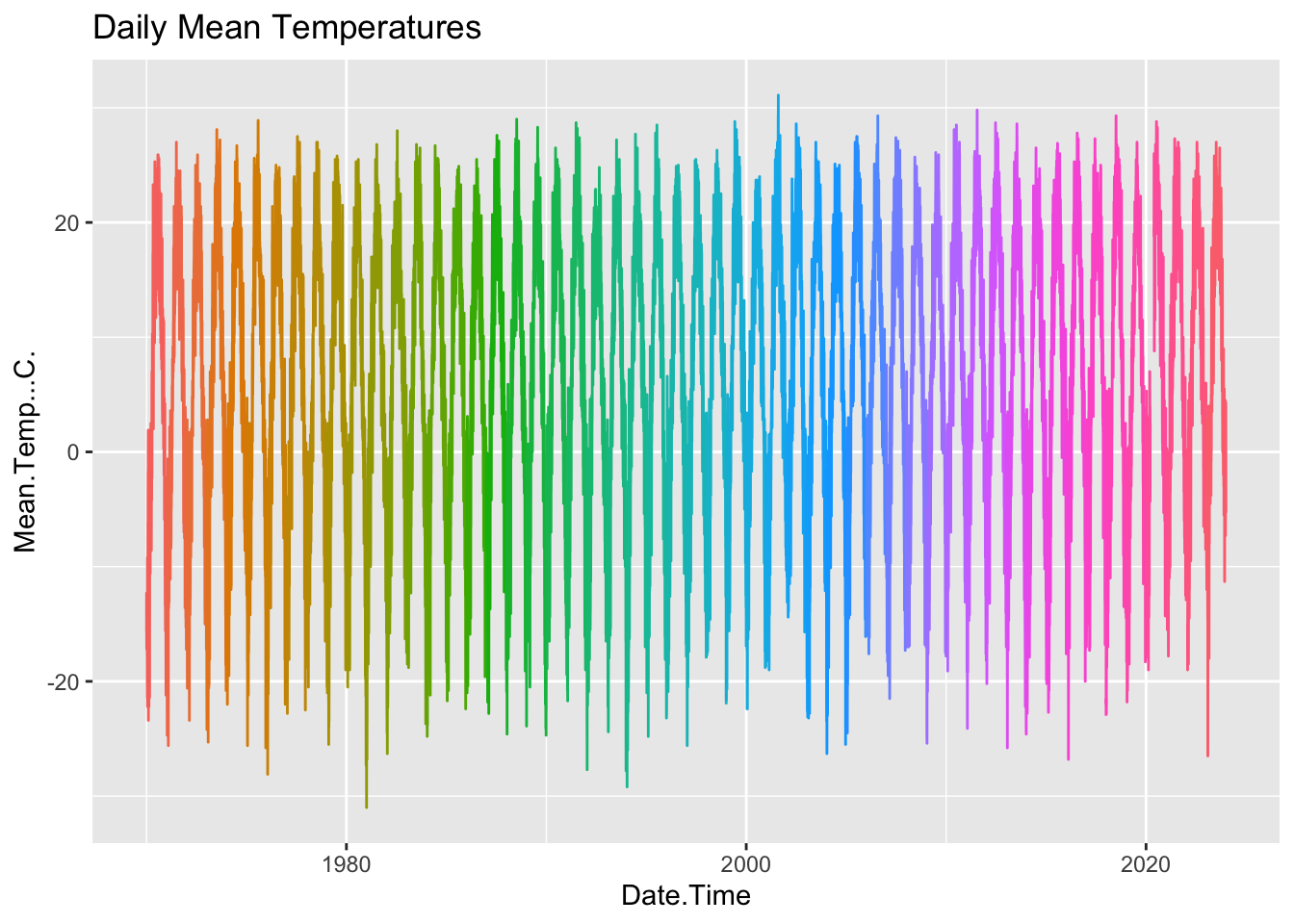
However it is tricky to see a change in a few degrees given the enormous seasonal variation. Let’s focus the plots:
july = df[df["Month"] == 7].groupby("Year").agg(
july_meanmax = pd.NamedAgg(column = "Max Temp (°C)", aggfunc = 'mean'))
january = df[df["Month"] == 1].groupby("Year").agg(
jan_meanmin = pd.NamedAgg(column = "Min Temp (°C)", aggfunc = 'mean'))
sb.lineplot(data = july,
x = "Year",
y = "july_meanmax")
sb.lineplot(data = january,
x = "Year",
y = "jan_meanmin")
plt.legend('', frameon = False)
plt.ylabel("Degrees C")
plt.title("Mean July Max and January Min Temperatures")
plt.show();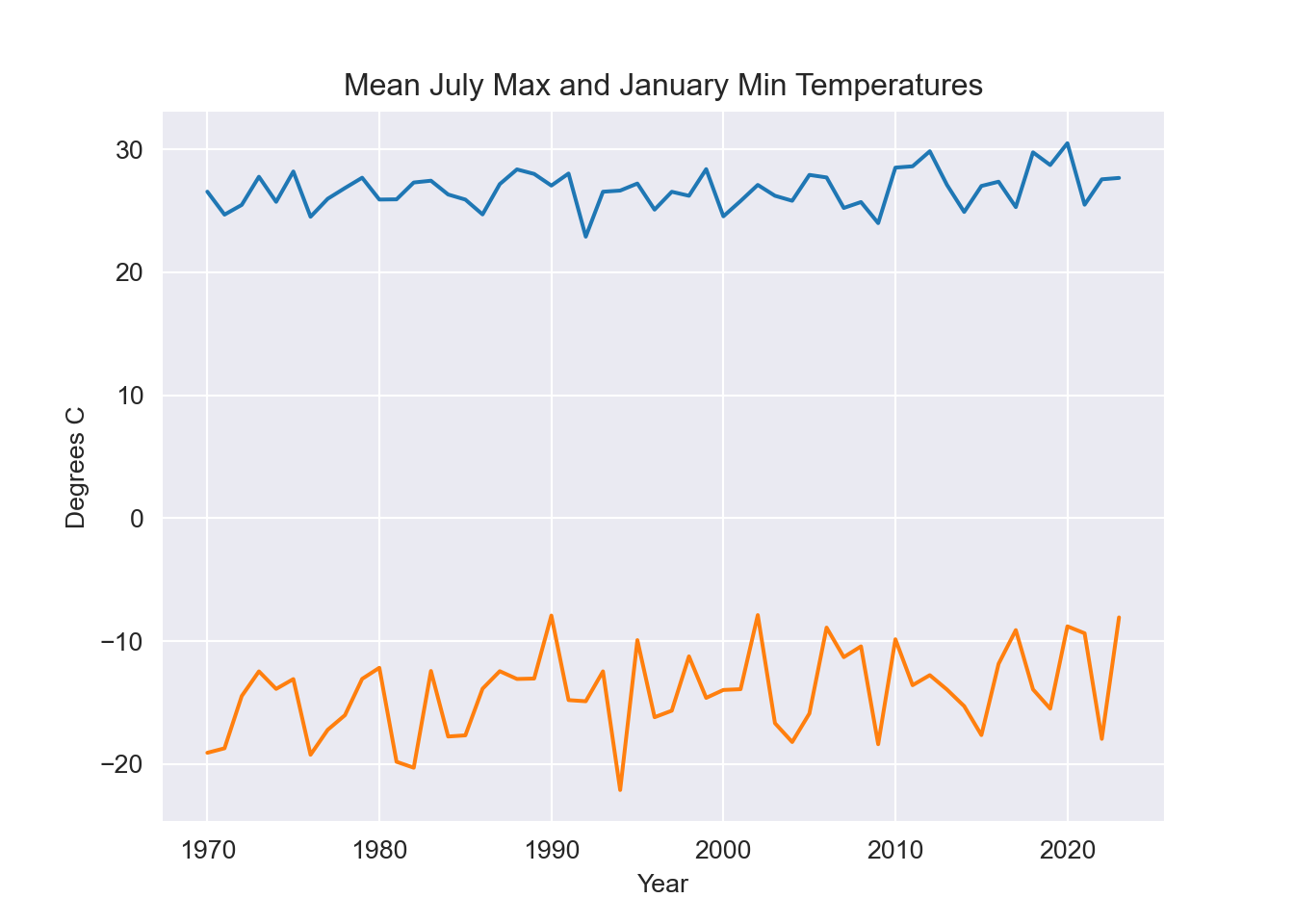
july["jan_meanmin"] = january["jan_meanmin"] # Add Jan column to july dataframe because seaborn takes data from a single dataframe
plt.clf()
sb.scatterplot(data = july,
x = "july_meanmax",
y = "jan_meanmin")
plt.legend('', frameon = False)
plt.title("January Min vs July Max Temperature by Year")
plt.show();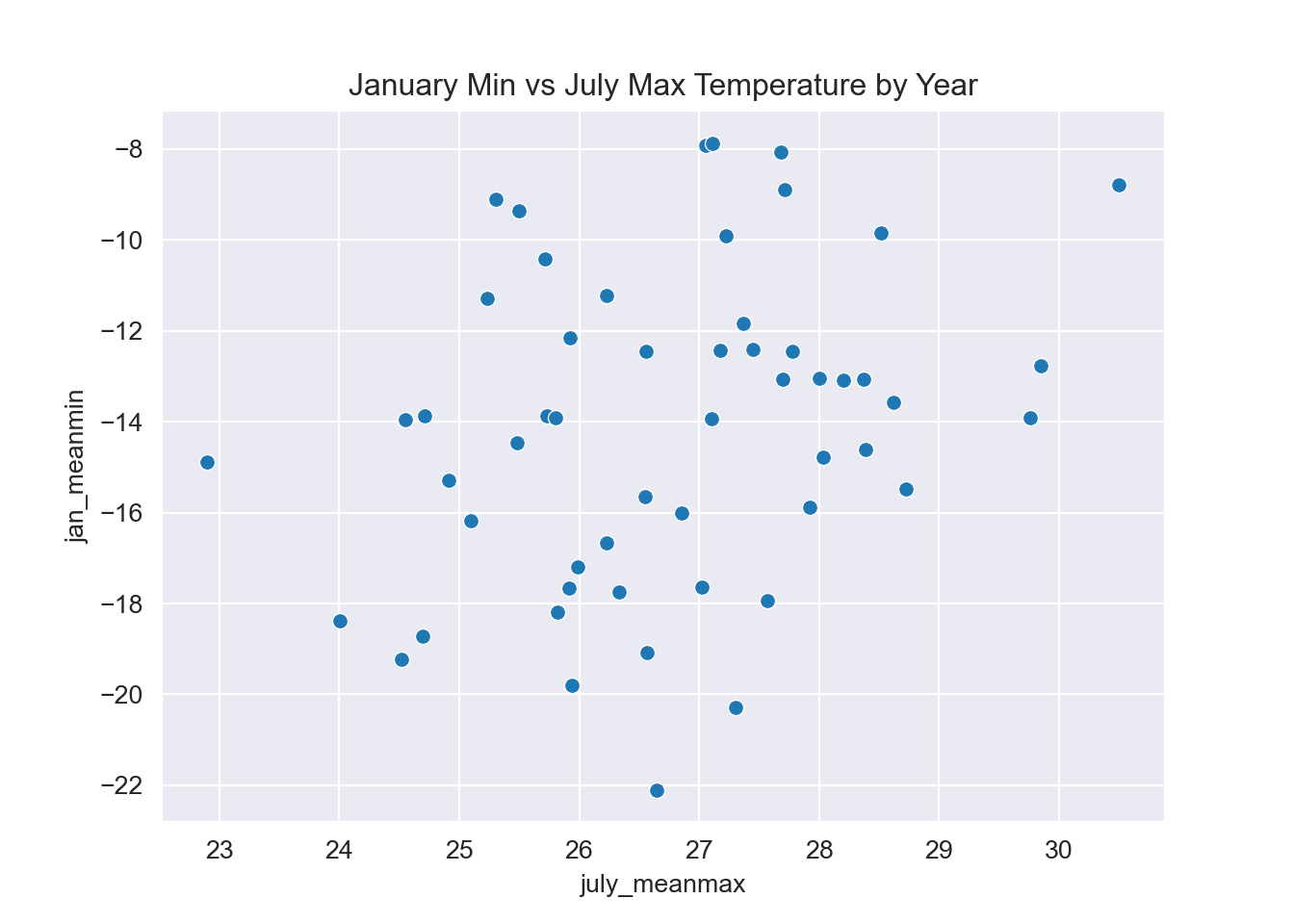
MeanOfJulyMax = data_daily |>
filter(Month == "07") |>
group_by(Year) |>
summarise(MeanOfJulyMax=mean(Max.Temp...C.)) |>
ungroup()
MeanOfJanMin = data_daily |>
filter(Month == "01") |>
group_by(Year) |>
summarise(MeanOfJanMin=mean(Min.Temp...C.)) |>
ungroup()
ggplot()+
geom_line(data = MeanOfJulyMax, aes(x=Year,y=MeanOfJulyMax , color="red"))+
geom_line(data = MeanOfJanMin, aes(x=Year,y=MeanOfJanMin,color="blue"))+
ggtitle("Means of the July Max and Jan Min Temperatures")+
labs(x = "Year", y="degrees C")+
theme(legend.position = "none") 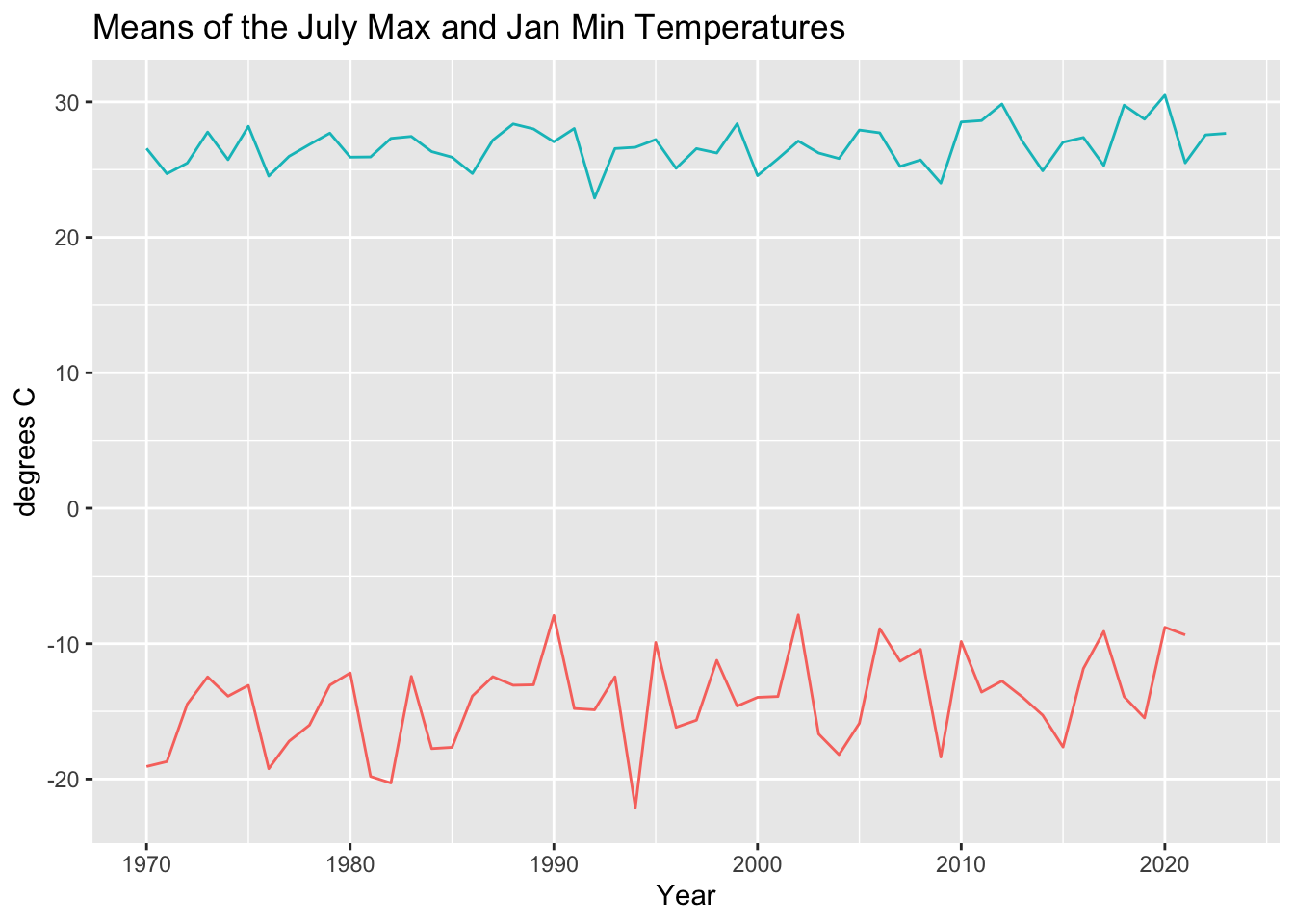
# merge the January minimum and the July maximum by matching year
MeanOfJulyMax |>
left_join(MeanOfJanMin) |>
ggplot()+
geom_point(aes(x=MeanOfJulyMax,y=MeanOfJanMin, colour = Year), size = 5)Joining with `by = join_by(Year)`Warning: Removed 1 row containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_point()`).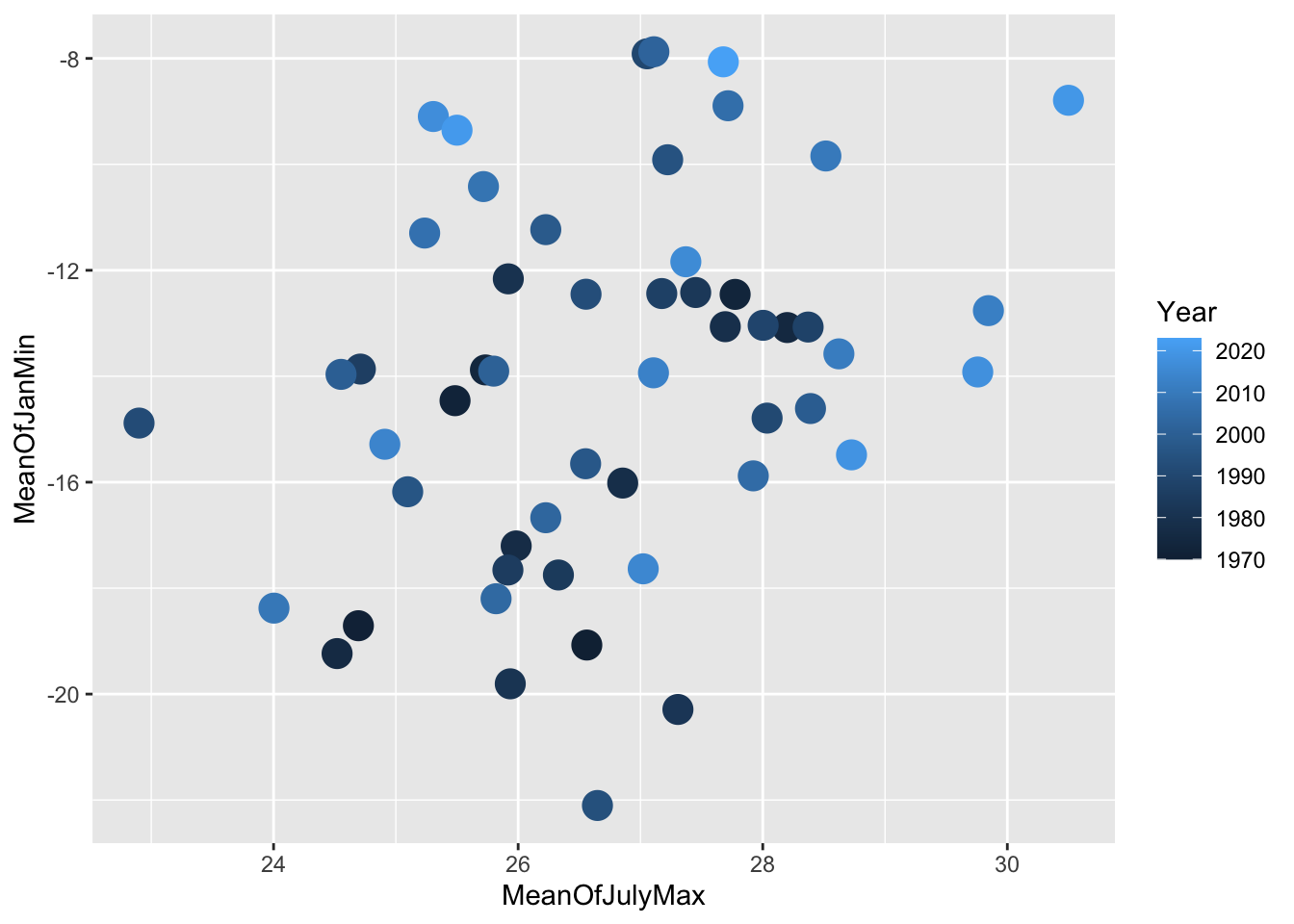
Loading and compiling the monthly data
Alternatively we can work with the monthly data. Note that the daily record started much later than the monthly record. Here we find and load the previously downloaded monthly data from the Data directory.
# Find name of the monthly csv file in the "Data" folder if you don't remember it from above
for f in os.listdir("Data/"):
if f.endswith("monthly.csv"):
filepath = f
break
ottawa_monthly =pd.read_csv("Data/"+filepath)
#convert the dates into valid date format by arbitrarily selecting the 1st of the month to complete the date
ottawa_monthly["Date/Time"] = pd.to_datetime(ottawa_monthly["Date/Time"])
plt.clf()
sb.lineplot(data = ottawa_monthly,
x = "Date/Time",
y = "Mean Temp (°C)",
hue = "Year")
plt.legend('', frameon = False)
plt.title("Monthly Mean Temperatures")
plt.xlabel("Year")
plt.ylabel("Degrees C")
plt.show();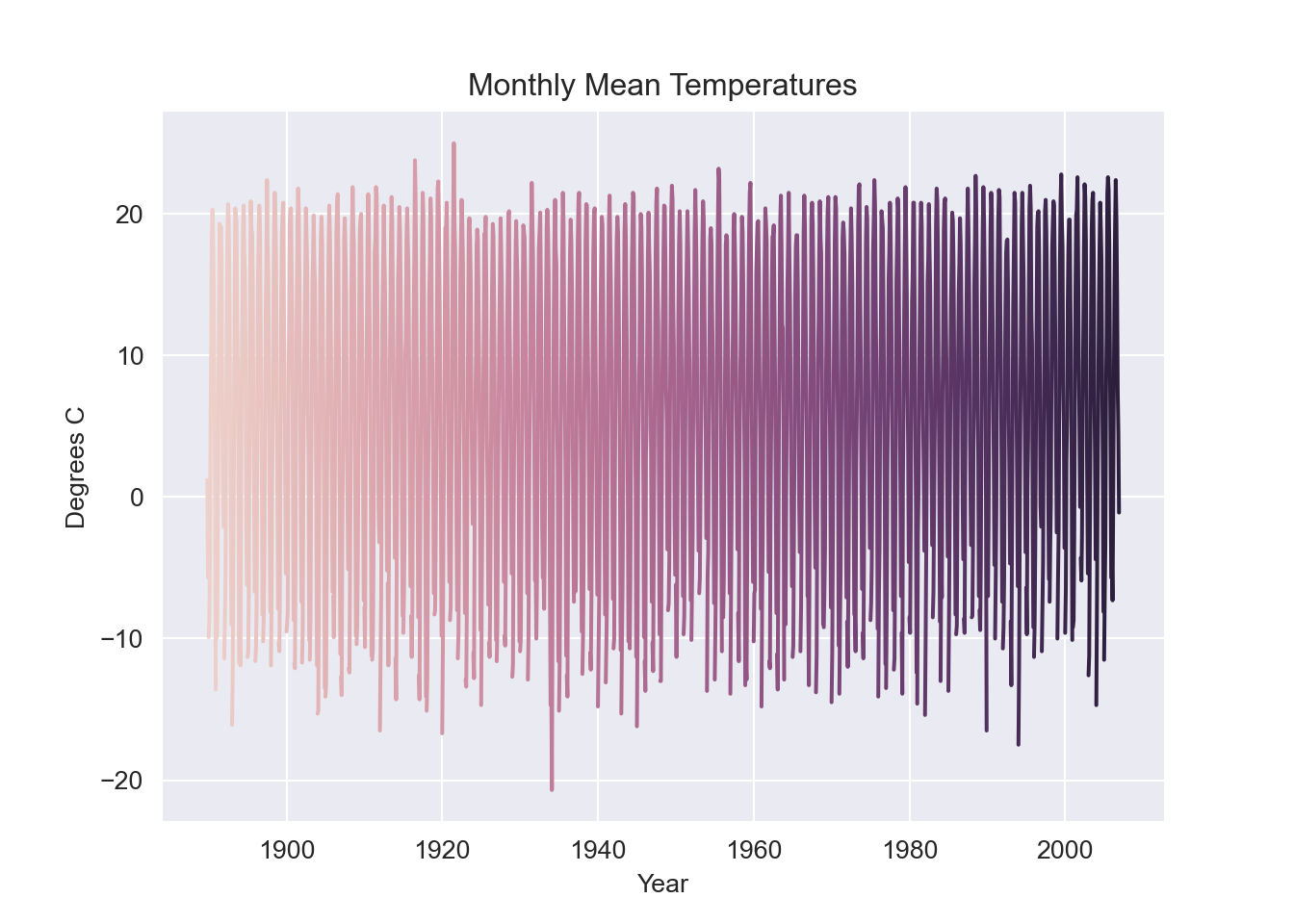
# Find name of the monthly csv file in the "Data" folder if you don't remember it from above
file2load = list.files("Data",pattern="monthly")
# Load and then convert all column names to nicer R syntax:
data_monthly = read_csv(paste0("Data/",file2load)) |>
rename_all(make.names)
#convert the dates into valid date format by arbitrarily selecting the 1st of the month to complete the date
data_monthly$Date.Time = as_date(data_monthly$Date.Time,format = "%Y-%m")
data_monthly |>
ggplot(
aes(x=Date.Time,y=Mean.Temp...C.,colour=factor(Year)))+
geom_line()+
ggtitle("Monthly Mean Temperatures")+
labs(x = "Year", y="degrees C")+
theme(legend.position = "none") Warning: Removed 10 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_line()`).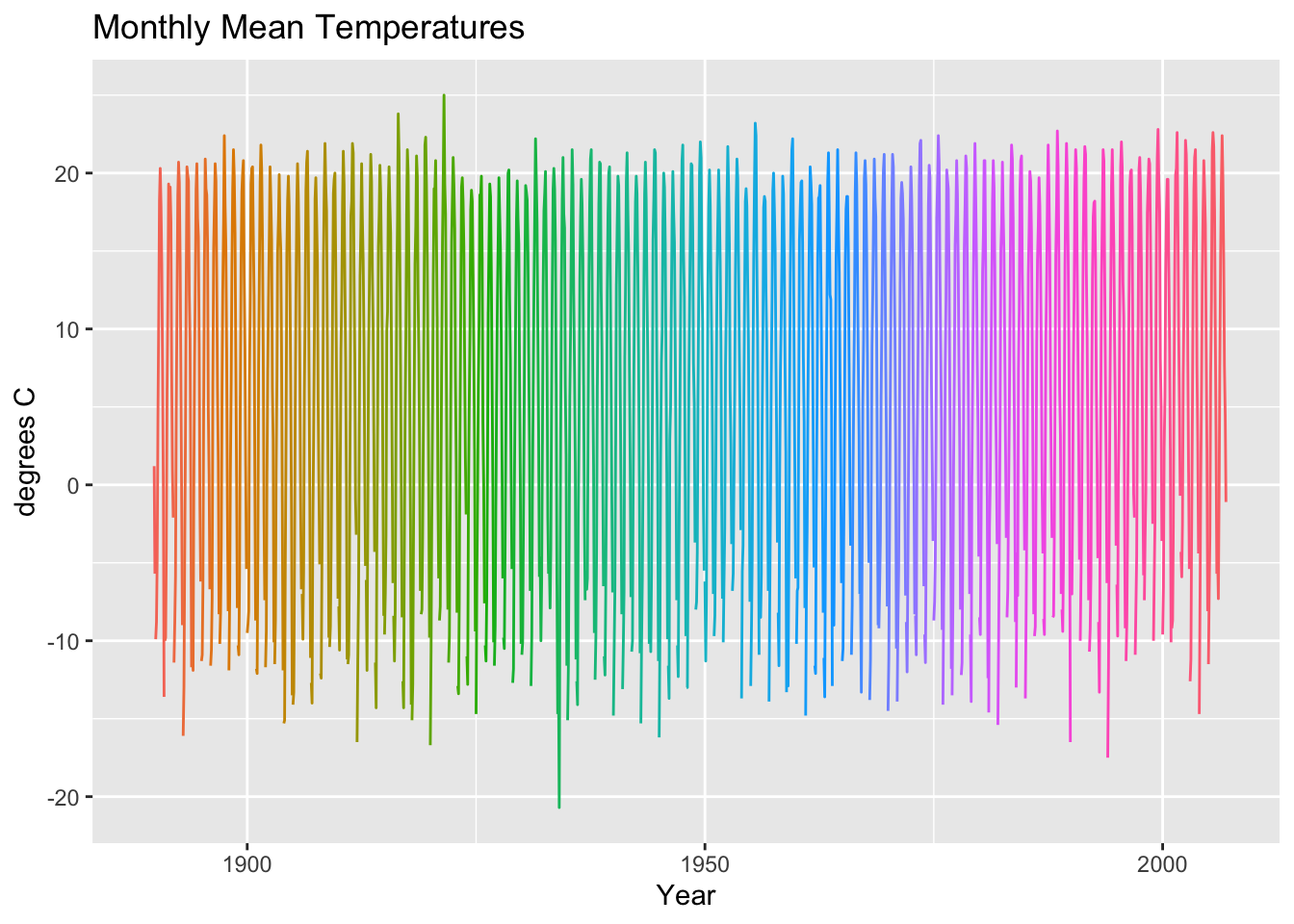
Data details
- Temperature units are in Celcius.
- Monthly values can be derived from daily ones.
- The speed of maximum gust is in kilometers per hour.
- Heating degree days are the number of degrees Celsius that the mean temperature is below 18 Celcius. This is a measure of heating requirement on that day.
- Cooling degree days are the number of degrees Celsius that the mean temperature is above 18 Celcius. This is a measure of the amount of cooling required on that day.
- The direction of the maximum gust is in tens of degrees, 9 means 90 degrees, which is an east wind, and 36 means 360 degrees implies a wind blowing from the geographic north pole.
- Other appeared letters like “M” indicates a missing value, “^” indicates the value displayed is based on incomplete data. All legend is shown at the end of the data source page.