


Next: Example 6
Up: Fseries_1
Previous: Note:
So far we have considered periodic functions of period 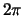 and their Fourier series. Similar formulae can be obtained for a piecewise continuous periodic function
and their Fourier series. Similar formulae can be obtained for a piecewise continuous periodic function 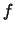 of an arbitrary period
of an arbitrary period 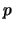 (
(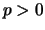 ). We consider the half-period
). We consider the half-period 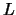 , such that
, such that 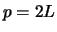 . Then we define the function
. Then we define the function
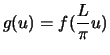 , which is also periodic and has the period
, which is also periodic and has the period 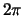 :
:
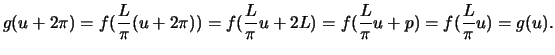 |
(10) |
Assume that 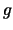 can be written as
can be written as
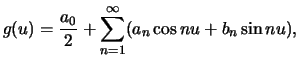 |
(11) |
with
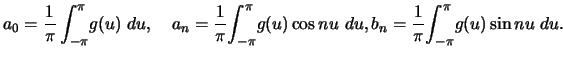
Then we change variables by setting
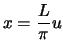 , and therefore
, and therefore
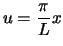 ,
,
so
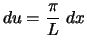 ,
and
,
and
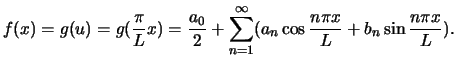 |
(12) |
The Fourier coefficient 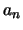 is calculated as follows:
is calculated as follows:
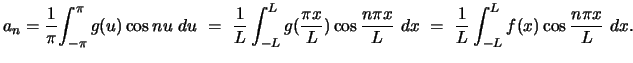 |
(13) |
Similarly,
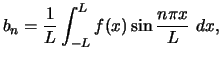 |
(14) |
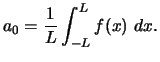 |
(15) |



Next: Example 6
Up: Fseries_1
Previous: Note:
Matthias Neufang
2002-09-18
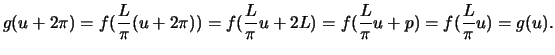
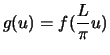 , which is also periodic and has the period
, which is also periodic and has the period ![]() can be written as
can be written as
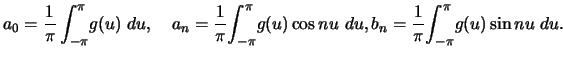
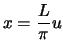 , and therefore
, and therefore
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
and
,
and
![]() is calculated as follows:
is calculated as follows: